Hypertransaminasemia is a frequent finding in pediatrics, which could reflect potentially treatable serious disease. The aim of this document is to establish, by reviewing the available evidence, a consensus for an adequate management of hypertransaminasemia, from its detection until the study is complete. To this end, a working group was formed with the participation of members of the Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (SEGHNP), the Spanish Association of Primary Care Pediatrics (AEPap) and the Spanish Society of Primary Care Pediatrics (SEPEAP). Twenty-one recommendations are established with a marked practical component that will be useful in hospital clinical practice and primary care.
La hipertransaminasemia es un hallazgo frecuente en pediatría, puede ser banal o reflejar enfermedad grave potencialmente tratable. El objetivo de este documento es establecer, mediante la revisión de la evidencia disponible, un consenso para un adecuado enfoque práctico desde la detección de la hipertransaminasemia hasta completar su estudio en la edad pediátrica. Para ello, se constituyó un grupo de trabajo con participación de miembros de la Sociedad de Gastroenterología, Hepatología y Nutrición Pediátrica (SEGHNP), Asociación Española de Pediatría de Atención Primaria (AEPap) y Sociedad Española de Pediatría de Atención Primaria (SEPEAP). Se establecieron 21 recomendaciones con el objetivo de que sirvan de utilidad en la práctica clínica habitual tanto en atención primaria como hospitalaria.
Transaminases are intracellular enzymes found in hepatocytes and other cells. The most important ones are aspartate aminotransferase (AST), also known as glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (GOT), which is less specific due to its ubiquity, and alanine aminotransferase (ALT), also known as glutamic-pyruvic transaminase (GPT), which is more specific to the liver.1–5
Hypertransaminasaemia can be detected in the evaluation of liver disease or can be an incidental finding in blood tests performed for other reasons.6 Mild elevations of transaminase levels frequently lead to performance of incomplete evaluations.7 Persistent hypertransaminasaemia calls for performance of a comprehensive evaluation to determine the specific aetiology.6–8
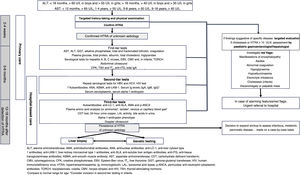
In developing this document, the objective was to establish the steps to take from the initial detection of hypertransaminasaemia in a blood test to the completion of the diagnostic process through a consensus process involving paediatricians specialised in primary care and in gastroenterology, hepatology and nutrition. It includes the sequence of tests to include in the initial diagnostic evaluation (Fig. 1). This document does not address the evaluation of patients with isolated cholestasis or cholestasis associated with hypertransaminasaemia, the diagnosis process for each specific disease once it is suspected, the treatment of the different causes of hypertransaminasaemia or the management of abnormal liver function or acute liver failure.
ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AMA, antimitochondrial antibodies; ANA, antinuclear antibodies; anti-LC-1, anti-liver cytosol type 1 antibodies; anti-LKM-1, liver-kidney microsomal type 1 antibodies; anti-SLA, anti-soluble liver antigen antibodies; anti-tTG, anti-tissue transglutaminase antibodies; ASMA, anti-smooth muscle antibody; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; CDT, carbohydrate deficient transferrin; CMV, cytomegalovirus; CPK, creatine phosphokinase; EBV, Epstein-Barr virus; fT4, free thyroxine; GGT, gamma-glutamyl transferase; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; HTRA, hypertransaminasaemia; Ig, immunoglobulin; LAL, lysosomal acid lipase; p-ANCA, perinuclear anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies; TORCH, toxoplasmosis, rubella, CMV, herpes simplex and HIV; TSH, thyroid-stimulating hormone.
1Compare to normal range for age. 2Consider inclusion in second-tier testing in infants.
A working group (WG) was established that comprised 8 members that represented the Sociedad Española de Gastroenterología, Hepatología y Nutrición (Spanish Society of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, SEGHNP), Asociación Española de Pediatría de Atención Primaria (Spanish Association of Primary Care Paediatrics, AEPap) and Sociedad Española de Pediatría Extrahospitalaria y Atención Primaria (Spanish Society of Outpatient and Primary Care Paediatrics, SEPEAP). The group broached 15 clinical questions regarding what, when and how to do from the moment of the initial detection of hypertransaminasaemia to the completion of its evaluation in both the primary care and hospital settings.
The WG conducted a systematic literature search in PubMed for articles published between January 2010 and January 2020 with the search terms “liver test” “liver disease” in patients aged 0–18 years, articles published at any time with the search terms “aminotransferase” “hypertransaminasemia” in ages 0–18 years, and articles published at any time with the terms “genetic liver disease” “histology liver disease”. We conducted a second search for articles published between January 2020 and September 2020 with the same approach. We used the Zotero 5.0 open-source citation management system. The search yielded 248 articles in English or Spanish, for which the group obtained the full text. Of this total, 113 were considered relevant to the consensus documents and selected because they were helpful in addressing the questions posed for development of the guideline.
Development of the documentThe WG answered each of the clinical questions (each of which was addressed by 2 members) based on the available evidence and with the aim of establishing a structured approach to the diagnostic evaluation of hypertransaminasaemia based on the consensus of the group. The group did not perform a systematic review or meta-analysis of the contemplated diagnostic tests. The full document was revised 5 times by every member of the group, with a virtual meeting conducted after each of the revisions through Gotomeeting (access granted by the SEGHNP and Zoom). All the recommendations presented in this document were reached by consensus and approved by the members of the group (informal consensus). The full consensus document can be consulted in the webpage of any of the participating professional associations.
Definition of hypertransaminasaemia and its main causesGiven the absence of a widely accepted abbreviation for hypertransaminasaemia, it was agreed that HTRA would be used for this document.
Hypertransaminasaemia (HTRA) is defined as elevation of serum levels of transaminases past the upper limit of normal (ULN)9 established in a healthy and representative sample of the population of interest. These levels exhibit substantial physiological variability within and between individuals. Their elevation reflects the lysis or increased permeability of the membrane of cells that contain them.2,5,6 In the paediatric population, through extrapolation of the threshold traditionally used in adults, HTRA is usually defined as levels greater than 40 U/L, but different authors have published thresholds that may differ to some extent and with some variations10–19 (Table 1). There is considerable overlap between healthy and unhealthy populations, which hinders the establishment of cut-off points with an adequate sensitivity and specificity.9 In addition, some authors note that in adolescence normal levels are too high and therefore this threshold loses sensitivity when used for initial screening of fatty liver or chronic hepatitis caused by hepatitis C virus (HCV), so that a lower ULN should be applied in these circumstances.10
Paediatric transaminase level ranges published by different authors.
| Author (year) | Values in U/L, by age range and/or sex | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fraser (2007) | Male and female adolescents | |||
| ALT LSN = 30 | ||||
| England (2009) | <18 months, male | <18 months, female | >18 months, male | female |
| ALT ULN = 60 | ALT ULN = 55 | ALT ULN = 40 | ALT ULN = 35 | |
| Lai (2009) | ALT 2.5−97.5 percentile = 8−38 | |||
| Schwimmer (2010) | Male adolescents | Female adolescents | ||
| ALT ULN = 26 | ALT ULN = 22 | |||
| Rodoo (2013) | 6 months-8 years, male | 6 months-8 years, female | 9−18 years, male | 9−18 years, female |
| ALT ULN = 23.4 | ALT ULN = 17.4 | ALT ULN = 30.6 | ALT ULN = 30.6 | |
| 6−12 months, male and female | 1−4 years, male and female | 5−8 years, male and female | 9−18 years, male and female | |
| AST ULN = 66 | AST ULN = 55.8 | AST ULN = 48 | AST ULN = 43.2 | |
| Zierk (2015) | ALT and AST expressed as a continuous reference spectrum in the form percentile curves (P2.5-P97.5) for age | |||
| Klietherme (2017) | Adolescents, male | Adolescents, female | ||
| ALT ULN = 28 | ALT ULN = 21−24 | |||
| Bussler (2018) | 11 months-16 years, male | 11 months-16 years, female | ||
| Several age ranges | Several age ranges | |||
| ALT ULN male = 29.9−38 | ALT ULN female = 24.2−31.7 | |||
| AST ULN male = 41.5−68.7 | AST ULN female = 35.2−62.9 | |||
| Kim (2018) | Adolescents, male | Adolescents, female | ||
| ALT ULN = 33 | ALT ULN = 25 | |||
| Liu (2019) | 9 age ranges, differences based on sex only in adolescents | |||
| ALT ULN = 39−56 | ||||
| AST ULN = 32−67 | ||||
ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; P, percentile; ULN, upper limit of normal.
There is no reliable correlation between the degree of transaminase elevation and its severity or prognosis. Nevertheless, very high levels are usually associated with extensive injury, which has led to the arbitrary categorization of HTRA into 3 degrees: mild (< 5 × ULN), moderate (=5−10 × ULN) and very high (>10 × ULN). On the other hand, based on experience and long-lasting consensus, HTRA is considered chronic if it lasts longer than 6 months.6
The detection of HTRA, transient as it may be in some cases, should be considered a potential marker of disease and be interpreted in the clinical context of the patient. Therefore, it should always be confirmed and monitored until the levels normalize or the cause is identified.1,20
In the paediatric population, there are multiple possible causes of HTRA, hepatic and extrahepatic, so its differential diagnosis is broad (Table 2).8,20 Isolated or disproportionate elevation of AST usually has an extrahepatic aetiology: difficult blood draw, haemolysis, rhabdomyolysis, etc. It may also be due to the formation of macro-AST.3
Causes of hypertransaminasaemia in the paediatric population.
| Hepatic | Hepatic | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Infectious | Acute hepatitis (A, B, C, D, E) and chronic hepatitis (B, C) Systemic with hepatic tropism: EBV, CMV, HSV, VZV, HIV, toxoplasmosis, SARS-CoV-2. Sepsis and bacteraemia. Brucellosis, leptospirosis, typhoid fever. | Neoplastic | Primary: liver tumour (hepatoblastoma, hepatocarcinoma) Secondary neuroblastoma, lymphoma, leukaemia, metastasis. |
| Hepatobiliary | Cholelithiasis, choledochal cyst | ||
| Cholestatic pattern of disease, require separate detailing and evaluation. | |||
| Other (more frequent in young children): respiratory and gastrointestinal viruses (adenovirus, RSV, parvovirus, echovirus, rotavirus), gastroenteritis caused by Salmonella, UTI | Traumatic | Obstetric trauma (subcapsular haematoma), abdominal trauma | |
| Miscellaneous | Chromosomal disorder (Turner syndrome), amyloidosis, sarcoidosis, Reye syndrome, CMPA (in infants), vascular diseases | ||
| Hepatotoxicity | Prescription drugs, illicit drugs, toxins, herbal and alternative medicine remedies. | ||
| Immune | Autoimmune hepatitis, autoimmune cholangitis. Liver disease associated with immune disorder: collagenosis and other | Gastrointestinal or systemic disease | Coeliac disease, thyroid dysfunction, cystic fibrosis, chronic inflammatory bowel disease, Shwachman-Diamond syndrome. |
| Obesity | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disorder (hepatic steatosis, steatohepatitis). | Extrahepatic | |
| Metabolic | Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, Wilson disease, galactosaemia, fructosaemia, tyrosinaemia, glycogenosis (I, III, IV, VI, IX), lipidosis (Gaucher, Niemann-Pick), fatty acid β-oxidation disorders, lysosomal acid lipase deficiency, congenital disorders of glycosylation, Inborn errors of bile acid synthesis, urea cycle disorders, lipoprotein metabolism disorders (HBL), porphyria, other. | Elevation of AST and ALT | Muscular and neuromuscular diseases (AST > ALT): Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy, caveolinopathies, limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, polymyositis, dermatomyositis, metabolic myopathies (glycogen storage disease type V or McArdle disease). Other disorders involving muscle: major trauma, high-degree burns, surgery, vigorous exercise. |
| Thyroid disorders: hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism. | |||
| Renal diseases. Adrenal insufficiency. Anorexia nervosa. | |||
| Ischaemic-vascular | Low cardiac output, hepatic artery or portal vein obstruction, congestive heart failure, Budd-Chiari syndrome. | Isolated AST elevation | Haemolysis: difficult blood draw, haemolytic disease. Heart disease (pericarditis, myocarditis, acute myocardial infarction). Isolated macroaspartasaemia. |
ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; CMPA, cow’s milk protein allergy; CMV, cytomegalovirus; EBV, Epstein-Barr virus; HSV, herpes simplex virus; HBL, hypobetalipoproteinaemia; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; RSV, respiratory syncytial virus; UTI, urinary tract infection; VZV, varicella-zoster virus.
*The most frequent aetiologies are presented in boldface.
The most frequent cause of acute mild-to-moderate elevation that normalises within 6 months is viral respiratory or gastrointestinal infection in infants, and infection by cytomegalovirus or Epstein-Barr virus in older children.8 A pharmacological or toxic aetiology should also be considered. The drugs most frequently involved in HTRA are antibiotic and antiepileptic agents, but there is a broad range of pharmaceuticals that can cause it. Other possible causative substances are illicit drugs (such as alcohol or cocaine), solvents, pesticides or natural remedies (such as St John’s wort, ephedra or gentian).
The main cause of persistent HTRA of hepatic aetiology in older children and adolescents is non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) associated with overweight or obesity.8
Recommendations:
- 1
We recommend the following ALT cut-off points for the healthy European paediatric population, stratified by age and sex: age less than 18 months, >60 U/L in boys and > 55 U/L in girls, and age greater than 18 months, >40 U/L in boys and >35 U/L in girls. We propose the following ALT thresholds for initial screening of hepatic steatosis or chronic hepatitis caused by HCV in adolescents: 26 U/L in male adolescents and 22 U/L in female adolescents.
- 2
We recommend the following AST cut-off points, stratified by age: >65 U/L up to age 12 months, >55 U/L for ages 1−4 years, >50 U/L for ages 5−8 years and >40 U/L for ages 9−18 years.
- 3
The aetiology of HTRA may be hepatic and/or extrahepatic. We recommend a stepwise diagnostic evaluation based on age and the most frequent hepatic and extrahepatic causes.
The history-taking and physical examination are the first tools to use in the diagnostic evaluation of HTRA.5,21,22 Their findings sometimes provide information on the aetiology or severity of the disease (Table 3).5,20–22 The history taking should include the personal and family medical history, use of pharmaceuticals or drugs, performance of vigorous activity, results of previous blood tests and systemic symptoms.20,22 The physical examination will include a thorough review of systems, as there is a broad range of extrahepatic conditions that may manifest with HTRA6 (Table 2).
Signs and symptoms in the history-taking and physical examination.
| Nonspecific manifestations | Asthenia, anorexia, nauseas, vomiting, abdominal distension, abdominal pain |
| Suggestive of liver disease | Hepatomegaly, jaundice, acholia, choluria |
| Suggestive of chronic liver disease | Telangiectasias, palmar erythema, malnutrition, ascites, splenomegaly, collateral vessels, gastrointestinal bleeding |
| Dysmorphic features | Characteristic phenotype (Alagille syndrome) |
| Neurologic manifestations | Irritability, changes in behaviour, changes in muscle tone, psychomotor retardation. |
| Manifestations of muscular involvement | Abnormal gait, myalgia, muscle hypertrophy or weakness. |
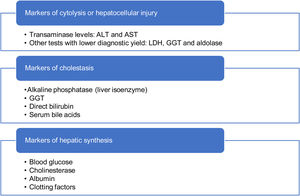
When it comes to diagnostic tests, the first step is to confirm the presence of HTRA.4 The comprehensive liver panel includes markers of hepatocellular liver injury, cholestasis and hepatic synthesis (Table 4).5,20 An abdominal ultrasound examination may be useful to assess liver and bile duct morphology, rule out tumours and, in adolescents with excess weight, indicate the possibility of fatty liver. Serological tests for viral detection will be performed based on the history of the patient.6
Many episodes of HTRA are self-limited, but there is variability in the time elapsed to resolution (weeks or months).6,22 There is no evidence to establish how much time should elapse before retesting. Traditionally, an interval of 2–4 weeks is recommended in the case of HTRA in the absence of any other warning signs.5,20–22 This interval should be individualised in the context of transient HTRA (associated with consumption of hepatotoxic pharmaceuticals or herbal remedies, infection, vigorous physical activity) likely to take longer to resolve.6,20
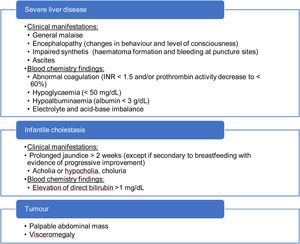
If additional warning signs are present (Table 5), the patient should be referred to a hospital on an urgent basis. It is particularly important to rule out acute liver failure (inability of the liver to perform its biosynthesis, regulation and detoxification functions).23 If there are signs of encephalopathy, impaired renal function requiring dialysis, haemodynamic instability or respiratory failure, the patient should be treated in an intensive care unit, and, in the presence of encephalopathy, hypoglycaemia, renal failure or an international normalised ratio (INR) greater than 2.5,24 transfer to a hospital that can perform liver transplantation should be contemplated.
Recommendations:
- 4
Performance of a thorough anamnesis and physical examination, which in some cases may reveal information that can guide the diagnosis and the assessment of severity.
- 5
We recommend considering detection of HTRA, even if transient, as a potential marker of disease to be evaluated taking into account the clinical context of the patient and with performance of a comprehensive liver panel for initial screening (Table 4).
- 6
Hypertransaminasaemia should always be confirmed. In the absence of other warning signs, we suggest performance of a confirmatory test 2–4 weeks after the initial detection. If a specific temporary cause is suspected, the follow-up test can be delayed to up to 8 weeks if resolution of the transient process is expected within that timeframe. If there are clinical or laboratory features suggestive of severity, the follow-up test will be performed on an urgent basis.
- 7
We recommend screening for the most frequent or relevant causes of HTRA by means of blood tests and an ultrasound examination (first-tier tests) following confirmation of HTRA or at the time the confirmatory test is performed (Table 6).
Table 6.First-, second- and third-tier tests.
First tier Comprehensive liver panel AST, ALT, GGT, alkaline phosphatase, total and fractionated bilirubin, coagulation study Blood chemistry Glucose, total protein, albumin, total cholesterol, triglycerides, CPK Acute infectious disease Viral serology tests for hepatitis A, B and C, Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus and, in infants, the TORCH test Imaging Abdominal ultrasound Other Thyroid function (TSH and fT4), coeliac disease (tissue transglutaminase IgA), total IgA Second tier Infectious disease Repeat serologic tests for hepatitis B and C and HIV. Autoantibodies ANA, ASMA, anti-LKM-1 Other Serum ceruloplasmin, serum alpha-1 antitrypsin, serum Ig levels (IgA, IgG and IgM)a Third tier Autoantibodies Anti-LC-1, anti-SLA, AMA, p-ANCA Imaging Abdominal Doppler ultrasound Other Plasma amino acid analysis (or ammonia)b, venous or capillary blood gas analysis,b lactate,b CDT test, alpha-1 antitrypsin phenotype, urine copper (24 -h urine), LAL activity, bile acids (plasma and/or urine), ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AMA, antimitochondrial antibodies; ANA, antinuclear antibodies; anti-LC-1, anti-liver cytosol type 1 antibodies; anti-LKM-1, liver-kidney microsomal type 1 antibodies; anti-SLA, anti-soluble liver antigen antibodies; ASMA, anti-smooth muscle antibody; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; CDT, carbohydrate deficient transferrin; CPK, creatine phosphokinase; fT4, free thyroxine; GGT, gamma-glutamyl transferase; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; Ig, immunoglobulin; LAL, lysosomal acid lipase; p-ANCA, perinuclear anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies; TORCH, toxoplasmosis, rubella cytomegalovirus, herpes simplex, and HIV; TSH, thyroid-stimulating hormone.
- 8
We recommend assessment of every warning sign that would warrant urgent referral to a hospital (severe liver disease, infantile cholestasis or suspected tumour) in ever follow-up visit. Children with cholestasis (excluding infants) should be referred for assessment on a priority basis.
- 9
If acute liver failure is suspected, we recommend considering admission to the intensive care unit and transfer to a hospital with an active paediatric liver transplantation programme.
In the absence of signs or symptoms that could guide the diagnostic evaluation, it is important to conduct an organised and systematic evaluation, with inclusion of specific diseases in the differential diagnosis.25–28
It must be taken into account that NAFLD is currently the most frequent cause of HTRA in children aged more than 10 years. Obesity and/or liver hyperechogenicity in the initial ultrasound scan suggest, but do not confirm, the presence of NAFLD and require evaluation according to the established protocol.29
Doppler ultrasonography allows diagnosis of diseases that could manifest with abnormal hepatic vascularization30 and is useful for screening of portal hypertension.31
The assessment of other diseases that are less frequent or that do not chiefly manifest with isolated HTRA should be personalised based on the age, clinical context, existing symptoms and associated clinical features (Table 7). Table 6 details the first, second and third-tier diagnostic tests.
Assessment of specific diseases.
| Diseases | Characteristics | Tests |
|---|---|---|
| Inborn errors of metabolism | Many are included in newborn screening protocols. | Review newborn screen results |
| Diagnosis guided by specialist in metabolic diseases | They are rarely asymptomatic, and their main manifestations (faltering growth, short stature, vomiting, psychomotor retardation, hepatomegaly, hypoglycaemia cholestasis, etc.) usually appear in infancy. | Plasma amino acids, ammonia, lactate, accumulation of metabolites in blood and/or urine, specific enzyme assays and genetic testing. |
| Infections | Patients in risk group for HBV or HCV with initial negative screen or immunocompromised patient. | PCR for detection of HBV DNA and HCV RNA |
| Opportunistic infections | ||
| Diagnosis guided by specialist in infectious disease | History of travel | Parasites and bacteria that with low prevalence Spain |
| Pancreatic involvement | Cystic fibrosis | Review newborn screen results |
| Sweat chloride test/CFTR gene | ||
| Shwachman-Diamond syndrome | Cytopenias | |
| Genetic testing | ||
| Macro-AST | Isolated, sustained and exclusive elevation of AST due to the presence of macroenzymes | Percent polyethylene glycol precipitable activity (%PPA) |
| Electrophoresis |
AST, aspartate aminotransferase; HBV, hepatitis B virus; HCV, hepatitis C virus.
Recommendations:
- 10
After performance of first-tier tests, if HTRA persists and its aetiology is unknown, we propose performance of laboratory tests for assessment of autoimmune hepatitis, Wilson disease, alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency, lysosomal acid lipase deficiency, bile acid synthesis disorders, congenital disorders of glycosylation and urea cycle defects and repetition of serology tests for hepatitis B virus (HBV) and HCV.
- 11
In children with sonographic features compatible with fatty liver and/or with excess weight, we recommend following the specific protocol for these diseases to complete the evaluation of HTRA.
- 12
In the case of persistent HTRA, we propose completing the imaging assessment with a liver Doppler ultrasound scan to evaluate hepatic venous and arterial vascularization.
- 13
In the presence of findings compatible with metabolic disease, and depending on the type of newborn screening performed, the clinical presentation, the age of the patient and the laboratory findings, we recommend performance of a targeted metabolomic analysis with participation of a specialist in metabolic disorders. In the cases of suspected cystic fibrosis, we recommend the sweat chloride test and, depending on the results, genetic testing to screen for variants in the CFTR gene.
- 14
In the case of children with risk factors for HBV or HCV (immunocompromised, from high-prevalence areas, of parents who are carriers of HBV or HCV), even if the hepatitis B surface antigen or HCV antibody test turn out negative, we recommend performance of PCR tests for detection of HBV DNA and HCV RNA.
- 15
In certain epidemiological situations, especially in children of immigrant origin, patients with suspected or known immunosuppression or undergoing evaluation of a systemic disease, the search for infectious aetiologies should be expanded in collaboration with a specialist in infectious disease.
- 16
In the case of isolated and sustained elevation of AST, we recommend testing for detection of macro-AST.
Specific studies have not been performed to validate the appropriate timing of follow-up tests in the management of HTRA. The specific circumstances of the patient are very important in determining when to perform follow-up tests. Normal transaminase levels at a single time point do not rule out liver disease, as some of these diseases have a fluctuating course.6 In addition, some diseases may manifest with mild transaminase elevation and still cause acute liver failure.6–32
In the absence of alarming findings (Table 5), patients should be referred to the hospital to complete the diagnostic evaluation or treatment when investigation or therapeutic options are exhausted in primary care or if there are findings indicative of severe disease (such as HTRA > 10 × ULN, cholestasis).20
Recommendations:
- 17
We recommend follow-up testing in 3–6 months in patients with unexplained HTRA that resolved after its detection, avoiding collection of the blood sample in the context of situations that may cause secondary hypertransaminasaemia (infection, medication, physical activity…).
- 18
In asymptomatic patients with HTRA, in the absence of red flags, we recommend performance of first- and second-tier tests in the first 3–6 months. If HTRA persists and its aetiology remains unknown, we suggest a comprehensive evaluation (first-, second- and third-tier tests) within 12 months of the initial detection of HTRA.
- 19
Patients with associated cholestasis or very high transaminase elevation (>10 × ULN) should be referred for assessment by a paediatric gastroenterologist/hepatologist on a priority basis.
- 20
In the absence of alarming signs, we recommend referral to a paediatric gastroenterologist/hepatologist of patients with HTRA and a suspected diagnosis requiring specific diagnostic procedures or treatment or with HTRA of unknown aetiology requiring performance of third-tier tests. The care setting where the second-tier tests are performed will depend on the organization, experience and resources of health care facilities in the region.
The results of previous tests, the phenotype of the patient and the study of the case with a geneticist will guide the selection of the genetic tests to be performed. At present, genetic testing is performed by means of next-generation sequencing (NGS) techniques. Next-generation sequencing allows detection of point mutations, microdeletions and intragenic insertions in several genes at once. The NGS tests used in clinical practice are targeted gene panels,33 clinical exome sequencing (CES), which may be targeted based on the key phenotypic features of the patient using the Human Phenotype Ontology (HPO) nomenclature34 and whole-exome sequencing (WES).35 Due to advances in molecular genetics and the increasing availability of these techniques, NGS will be used increasingly frequently and at earlier stages in clinical practice.
Liver biopsy (LB)Since this is an invasive procedure, it is only performed after an exhaustive initial evaluation with non-invasive methods. The ultrasound-guided needle biopsy of the liver is the criterion standard procedure for sampling liver tissue, using cutting or suction needles of varying gauge based on age.36 Persistent HTRA is the main indication for performance of LB in children.37 The right time to perform it is not as clearly established. Some authors have reported a low diagnostic yield of LB in the case of sustained HTRA of unknown aetiology, and performance of this procedure could be delayed to 14–16 months after initial detection of HTRA.8 The parents or legal guardians must be informed of the potential benefits and risks of the procedure based on the nature of the liver disorder experienced by the child.
The LB specimen can provide information on specific pathological and histological features of different liver diseases.38,39 This technique is also useful in the prognostic assessment of chronic liver disease through the determination of histological activity indices (inflammation, fibrosis, necrosis, steatosis etc). Different techniques may be used in the histological examination: basic staining with haematoxylin and eosin, special histochemical stains and immunostains or electron microscopy.37 Adequate communication between the pathology and clinical teams is crucial to ensure the correct processing and assessment of histological samples.
In recent years, non-invasive techniques have been developed to assess liver fibrosis by ultrasound elastography. Although this approach provides relevant information in the followup, due to the absence of established normal ranges validated in the paediatric population or specific cut-off values for the different diseases that may be present, ultrasound elastography cannot currently replace performance of a LB.40
Recommendations:
- 21
In the case of persistent HTRA without an aetiological diagnosis, genetic testing should be performed in collaboration with specialists in clinical genetics. In these patients in whom HTRA is the only warning sign, we recommend clinical exome sequencing.
- 22
We recommend performance of an additional LB (preferably guided by ultrasound) at 12–18 months from initial detection of asymptomatic and persistent HTRA, in the absence of other warning signs, in patients in whom the previous diagnostic evaluation did not establish the aetiology of HTRA.
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Please cite this article as: Arnal IR, Andrade JR, Hally MM, Baviera LCB, Tirado DG, Martín SHC, et al. Actuación diagnóstica ante hipertransaminasemia en pediatría: documento de consenso de Sociedad Española de Gastroenterología, Hepatología y Nutrición Pediátrica (SEGHNP), Asociación Española de Pediatría de Atención Primaria (AEPap) y Sociedad Española de Pediatría de Atención Primaria (SEPEAP). An Pediatr (Barc). 2022;96:448.