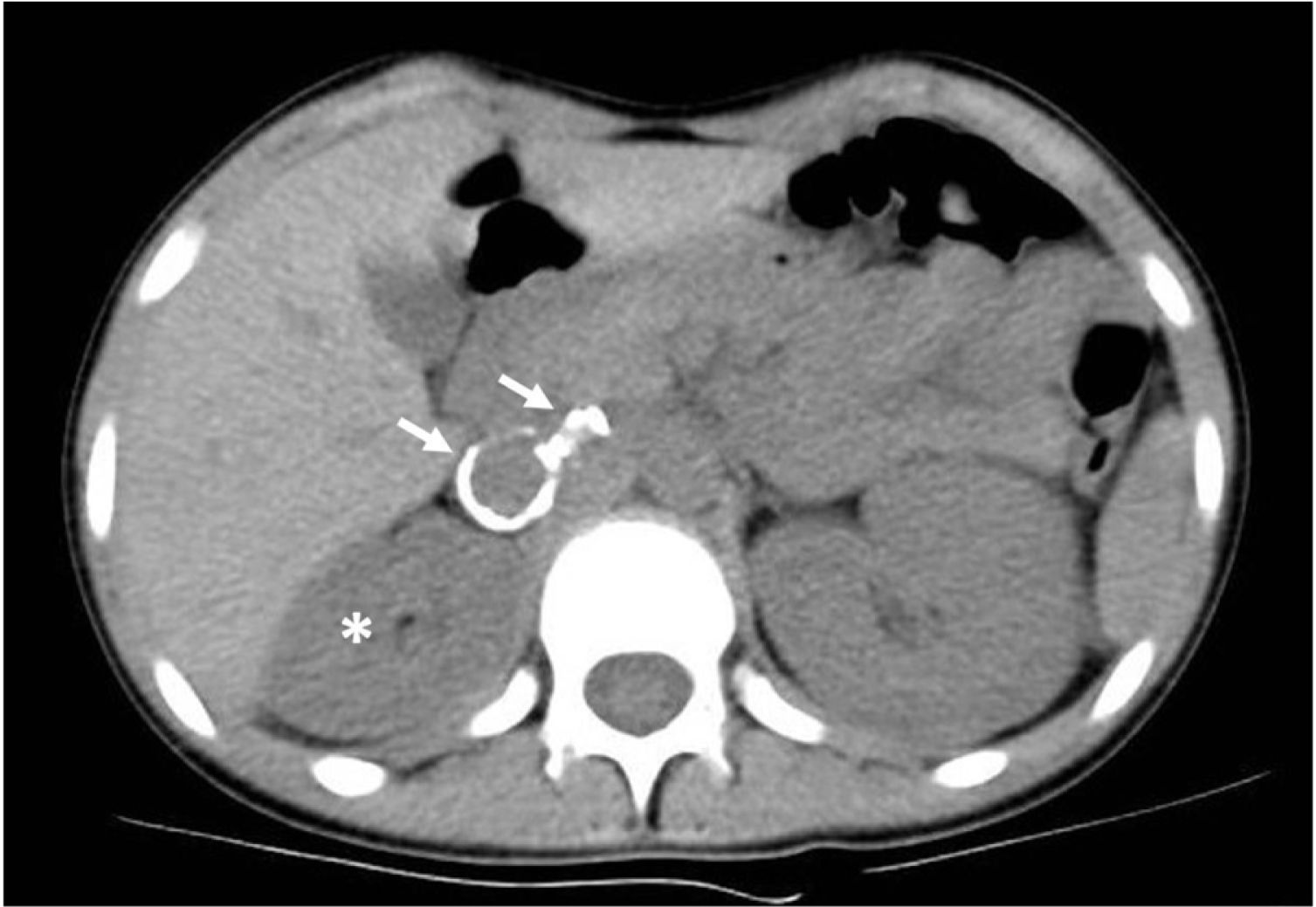
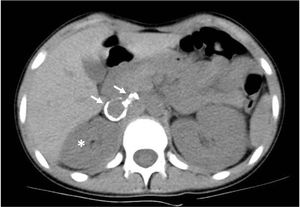
A girl aged 13 years presented with asthenia, decreased appetite, dizziness and abdominal pain of 2 months’ duration. The chief finding of the physical examination were hypertension (HTN) with a blood pressure of 200/135mmHg. The Doppler ultrasound showed an atrophied right kidney with aneurysms in the right renal artery, confirmed by CT angiography (Fig. 1) and arteriography. There was end-organ damage: acute renal failure (peak creatinine, 1.45mg/dL), retinopathy, cardiomyopathy and transient ischaemic attacks in the white matter. The presence of aneurysms in other locations was ruled out with whole-body magnetic resonance angiography.
The patient did not meet the diagnosis criteria for Marfan, Ehlers-Danlos or Grange syndrome, polyarteritis nodosa, tuberous sclerosis or neurofibromatosis. There were no other signs suggestive of atherosclerosis.
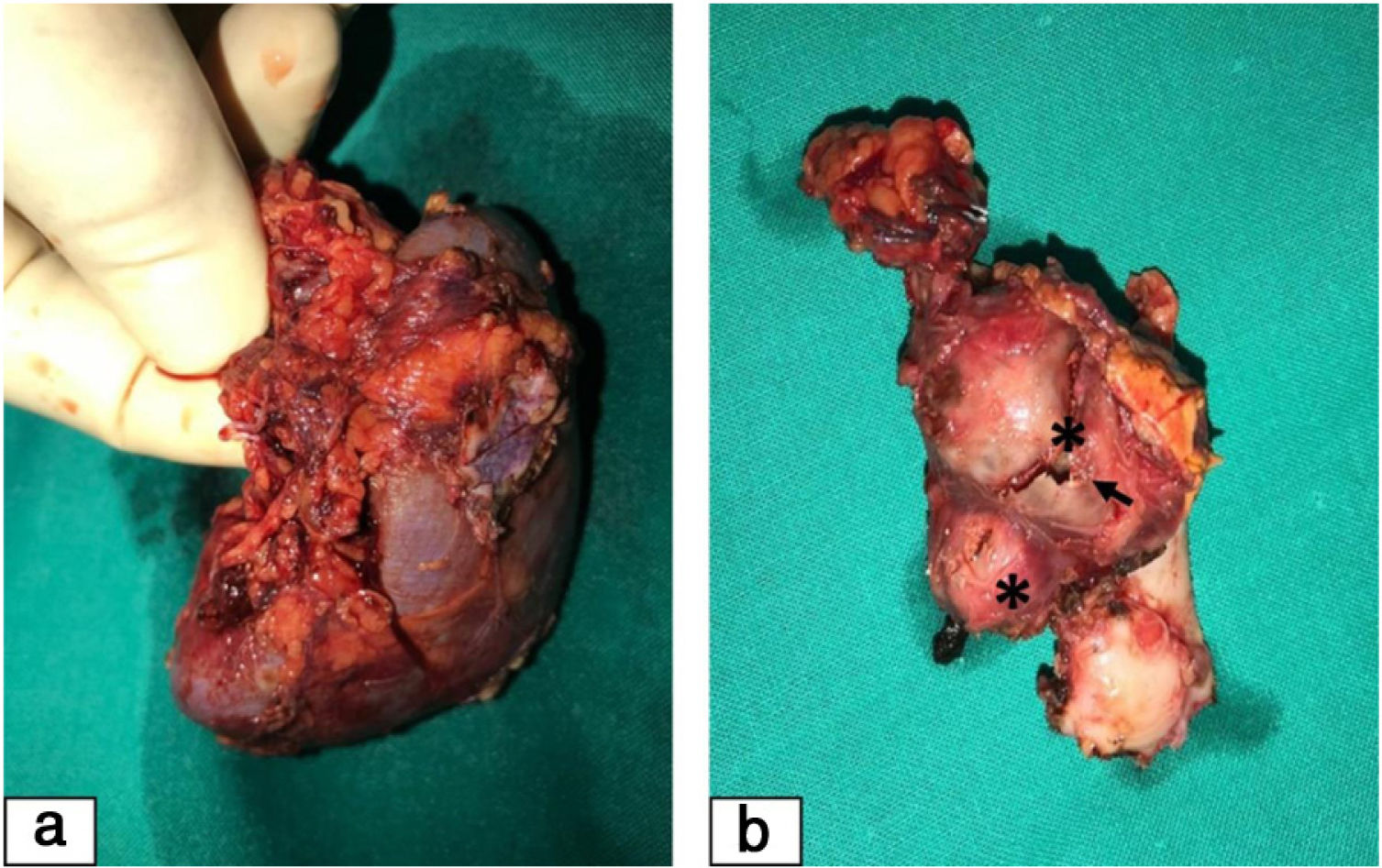
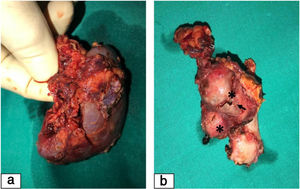
The approach selected initially was angioplasty with stenting, which could not be carried out due to spontaneous embolization. Given the persistence of HTN and the near-total dysfunction of the right kidney, the decision was made to perform right nephrectomy (Fig. 2), which achieved progressive improvement of blood pressure and renal function. The histological features were compatible with fibromuscular dysplasia. At 2 years of follow-up, her blood pressure is in the normal range without treatment, and the glomerular filtration rate calculated with the modified Schwartz formula is 66mL/min/1.73m2.
Fibromuscular dysplasia is a disease that is rare in children of unknown aetiology and prevalence and characterised by the presence of non-inflammatory segmental stenosis in arteries of small and medium calibre, and it most frequently involves the renal artery.1,2
Despite its low sensitivity, Doppler ultrasound is useful in the initial diagnosis of renovascular HTN. Computed tomography angiography and MR angiography offer a greater sensitivity. Renal arteriography is the gold standard of diagnosis.1,3 Treatment consists in controlling the blood pressure and, in select cases with refractory HTN, angioplasty.1,3
Conflicts of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Previous meeting: This case was presented at the XLIV National Congress of Paediatric Nephrology, May 15–18, 2019, Badajoz, Spain.