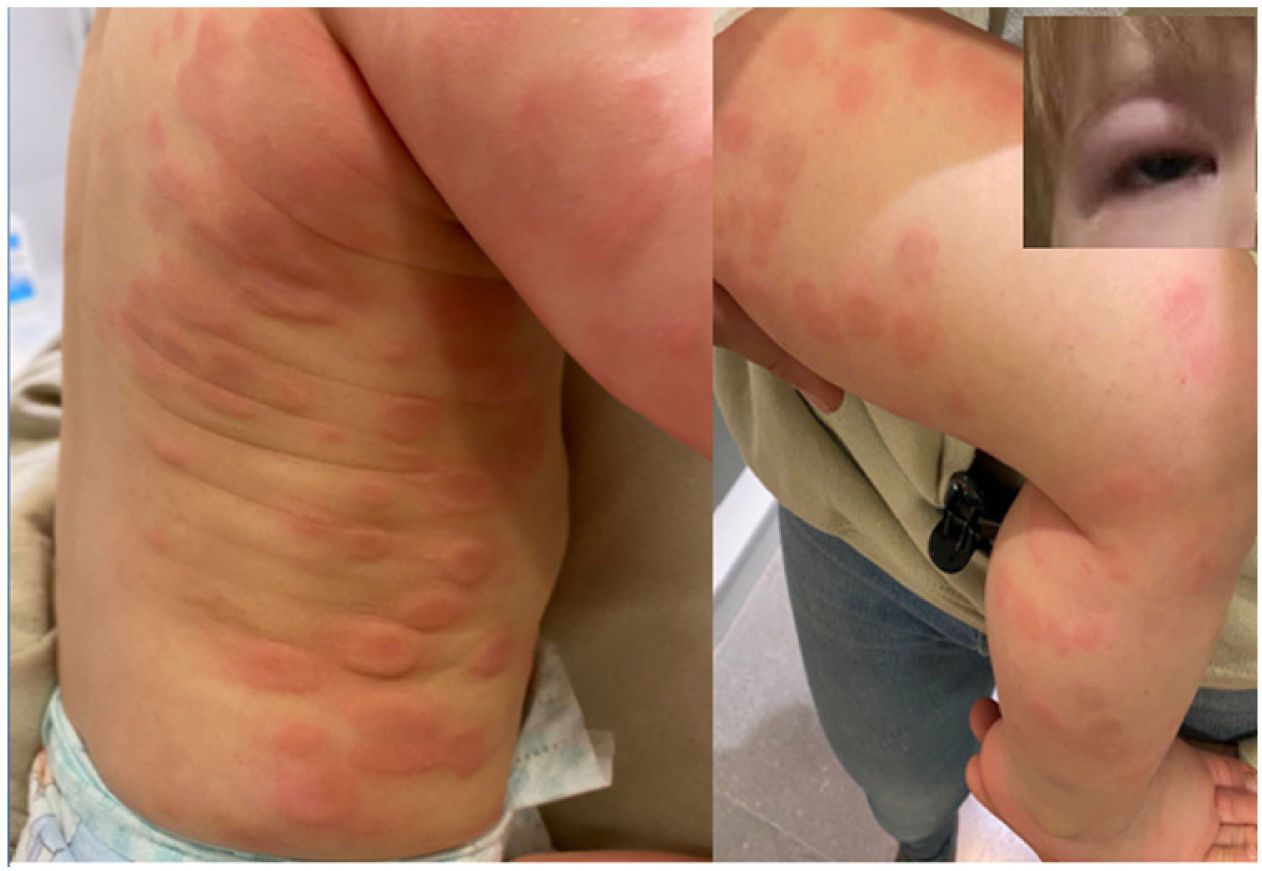
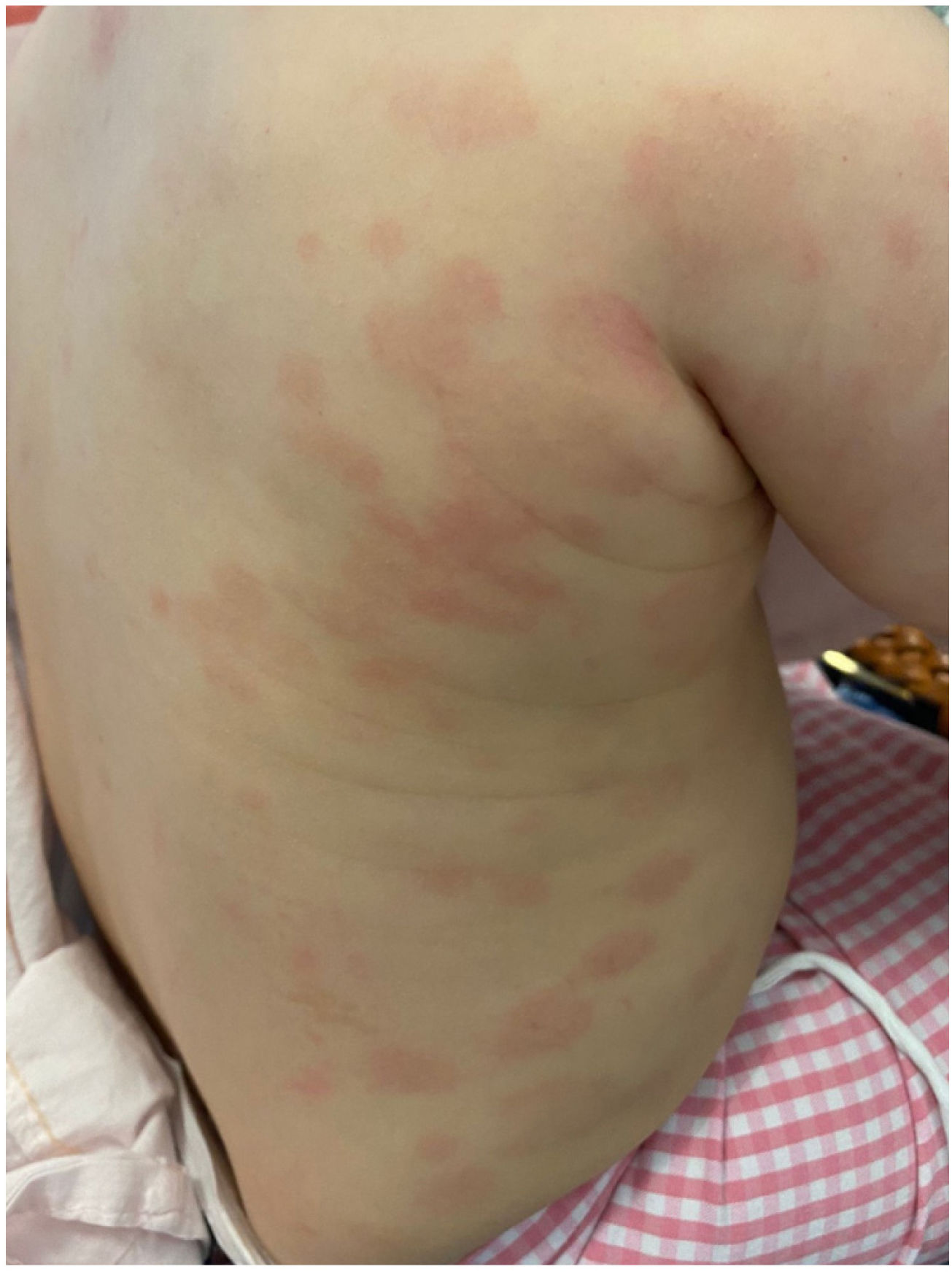
A boy aged 15 months presented with exanthema of several days’ duration. He had been vaccinated against varicella 14 days prior. He appeared to be in excellent general health, had swelling of the eyelids and feet, and generalised exanthema with 2 types of elements: (1) erythematous macules, appearing as hives or plaques in some areas, with a purplish centre in some and pale centre in others, without vesicles or central necrosis (Fig. 1), and (2) disseminated petechiae (Fig. 2). In the complete blood count, the platelet concentration was 30 000 platelets/μL; the remaining counts and levels of acute phase reactants were normal and virus detection tests negative.
The patient received 1 dose of prednisolone, and 24 h later there was marked improvement of the cutaneous manifestations (Fig. 3) and the platelet count had increased to 47 000 platelets/μL. The platelet count was normal 10 days later.
Urticaria multiforme and thrombocytopenic purpura are diseases that may be, although infrequently, triggered by vaccination.1,2 The combined presence of both is surprising, and we were not able to establish a causal relationship. The former is very similar to erythema multiforme, but does not involve the entire body. Vaccine-induced thrombocytopenic purpura is usually self-limited but still carries a risk of bleeding.1,3 The care team discussed whether it would be appropriate to administer the second dose of the vaccine due to the risk of thrombocytopenia; although this risk is generally low,3 given the significant symptoms in the patient and the concern of the family, the care team recommended against it.
FundingThis research did not receive any external funding.